-

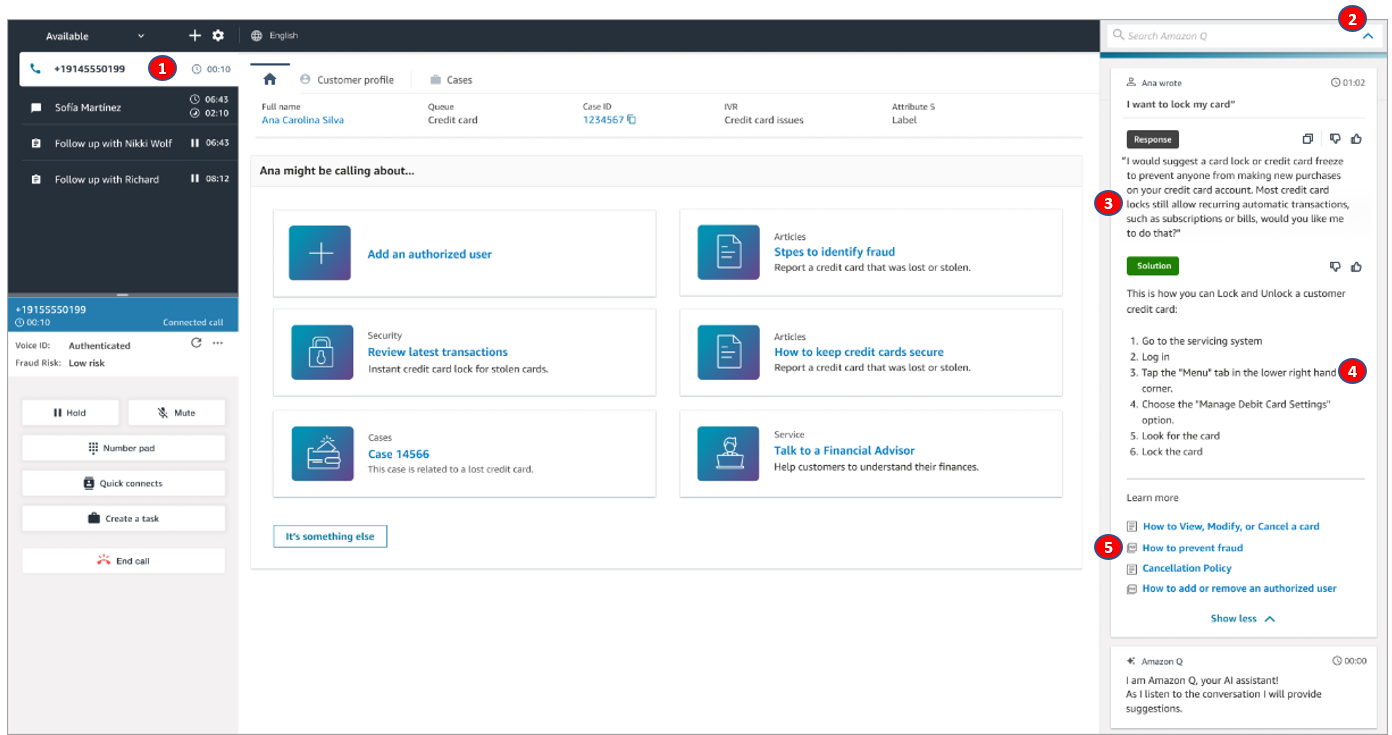
ElasticSearch Portal
$299.00 -

Cloud Networking Backbone
$142.00 -

Distributed Cloud Desktop
$34.99 -

Domains & Gateways
$12.99 -

RPM Cloud Server
$39.99 -

Enterprise Workmail
$24.99 -

Chat Bot Module for Customer Support
$34.99 -
Contact Center Prime with Customer Sentiment Analysis
$79.99 -

Standard Contact Center
$39.99 -

Growth Contact Center with SMS
$61.99
Identify Java nested dependencies with Amazon Inspector SBOM Generator
Java archive files (JAR, WAR, and EAR) are widely used for packaging Java applications and libraries. These files can contain various dependencies that are required for the proper functioning of the application. In some cases, a JAR file might include other JAR files within its structure, leading to nested dependencies. To help maintain the security and stability of Java applications, you must identify and manage nested dependencies.
This challenge arises from several factors:
Nested dependencies occur when a library or module that is required by your application relies on additional libraries or modules. This is a common scenario in modern software development because developers often use third-party libraries to build upon existing solutions and to benefit from the collective knowledge of the open-source community.
In the context of JAR files, nested dependencies can arise when a JAR file includes other JAR files as part of its structure. These nested files can have their own dependencies, which might further depend on other libraries, creating a chain of dependencies. Nested dependencies help to modularize code and promote code reuse, but they can introduce complexity and increase the potential for security vulnerabilities if they aren’t managed properly.
Consider the following examples, which depict a typical file structure of a Java application to illustrate how nested dependencies are organized:
This structure includes the following files and dependencies:
This structure illustrates how a Java application might include nested dependencies, with Log4J nested within other libraries. The actual nesting and dependencies will vary based on the specific libraries and versions that you use in your project.
This structure includes the following files and dependencies:
This structure includes the following files and dependencies:
Here are some reasons why it’s important to understand the dependencies that are consumed within a JAR file:
These examples underscore that you need to have deep visibility into JAR file contents to help protect against immediate threats and help ensure long-term application health and compliance.
When analyzing Java applications for nested dependencies, one of the main challenges is that existing tools can’t efficiently narrow down the exact location of these dependencies. This issue is particularly evident with tools such as mvn dependency:tree, OWASP Dependency-Check, and similar dependency analysis solutions.
Although tools are available to analyze Java applications for nested dependencies, they often fall short in several key areas. The following points highlight common limitations of these tools:
A key feature of Sbomgen is its ability to provide explicit paths to each dependency.
For example, given a compiled jar application MyWebApp-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar, users can run the following CLI command with Sbomgen:
The output should look similar to the following:
In this output, the amazon:inspector:sbom_collector:path property is particularly significant. It provides a clear and complete path to the location of the specific dependency (in this case, log4j-to-slf4j) within the application’s structure. This level of detail is crucial for several reasons:
After you identify the nested dependencies in your Java JAR files, you should verify whether these dependencies are outdated or vulnerable. Amazon Inspector can help you achieve this by doing the following:
By integrating Amazon Inspector into your software development lifecycle, you can continuously monitor your Java applications for vulnerable nested dependencies and take the necessary steps to help ensure that your application remains secure and compliant.
To help secure your Java applications, you must manage nested dependencies. Amazon Inspector provides an automated and efficient way to discover and mitigate potentially vulnerable dependencies in JAR files. By using the capabilities of Amazon Inspector, you can help improve the security posture of your Java applications and help ensure that they adhere to best practices.
Chi is a Security Researcher who helps ensure that AWS services, applications, and websites are designed and implemented to the highest security standards. He’s a SME for Amazon Inspector and enthusiastically assists customers with advanced issues and use cases. Chi is passionate about information security — API security, penetration testing (he’s OSCP, OSCE, OSWE, GPEN certified), application security, and cloud security.
Anything we Missed?
- Home ,
- Shop ,
- Cart ,
- Checkout ,
- My account

PO Box 4942 Greenville, SC 29609
Infrastructure Security News
-
AWS recognized as an Overall Leader in 2024 KuppingerCole Leadership Compass for Policy Based Access Management
Figure 1: KuppingerCole Leadership Compass for Policy Based Access Management The repo...Read more -


Modern web application authentication and authorization with Amazon VPC Lattice
When building API-based web applications in the cloud, there are two main types of comm...Read more -


Enable multi-admin support to manage security policies at scale with AWS Firewall Manager
These are some of the use cases and challenges faced by large enterprise organizations ...Read more -


AWS re:Invent 2023: Security, identity, and compliance recap
At re:Invent 2023, and throughout the AWS security service announcements, there are key...Read more -


AWS HITRUST Shared Responsibility Matrix for HITRUST CSF v11.2 now available
SRM version 1.4.2 adds support for the HITRUST Common Security Framework (CSF) v11.2 as...Read more -


AWS completes the 2023 South Korea CSP Safety Assessment Program
The audit scope of the 2023 assessment covered data center facilities in four Availabil...Read more -


AWS Customer Compliance Guides now publicly available
CCGs offer security guidance mapped to 16 different compliance frameworks for more...Read more -


How to migrate your on-premises domain to AWS Managed Microsoft AD using ADMT
February 2, 2024: We’ve updated this post to fix broken links and added a note on migra...Read more -


How to automate rule management for AWS Network Firewall
For this walkthrough, the following prerequisites must be met: Figure 1 describes how ...Read more -


2023 C5 Type 2 attestation report available, including two new Regions and 170 services in scope
AWS has added the following 16 services to the current C5 scope: AWS strives to contin...Read more -


How to enforce creation of roles in a specific path: Use IAM role naming in hierarchy models
A fundamental benefit of using paths is the establishment of a clear and organized orga...Read more -


Latest PCI DSS v4.0 compliance package available in AWS Artifact
Want more AWS Security news? Follow us on Twitter. Nivetha is a Security Assurance Man...Read more -


SaaS access control using Amazon Verified Permissions with a per-tenant policy store
Access control is essential for multi-tenant software as a service (SaaS) applications....Read more -


Identify Java nested dependencies with Amazon Inspector SBOM Generator
Java archive files (JAR, WAR, and EAR) are widely used for packaging Java applications ...Read more -


How AWS can help you navigate the complexity of digital sovereignty
Digital sovereignty means different things to different people, and every country or re...Read more -


Data masking and granular access control using Amazon Macie and AWS Lake Formation
Companies have been collecting user data to offer new products, recommend options more ...Read more -


Export a Software Bill of Materials using Amazon Inspector
Customers have asked us to provide additional software application inventory collected ...Read more -


2023 PiTuKri ISAE 3000 Type II attestation report available with 171 services in scope
The following are the 17 additional services now in scope for the 2023 Pitukri report: ...Read more -


AWS completes the first cloud audit by the Ingelheim Kreis Initiative Joint Audits group for the pharmaceutical and life sciences sector
As customers embrace the scalability and flexibility of AWS, we’re helping them evolve ...Read more -


AWS renews K-ISMS certificate for the AWS Asia Pacific (Seoul) Region
This certification helps enterprises and organizations across South Korea, regardless o...Read more
© Cloud Level | All rights reserved | made on a by 